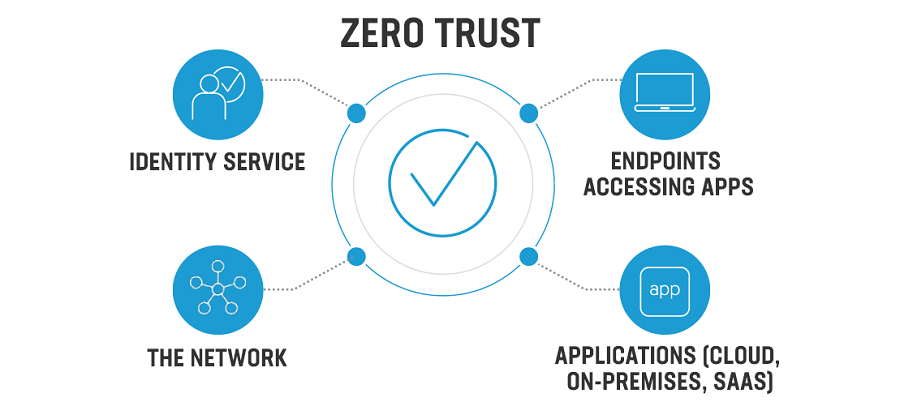
Key components of zero trust network access system – ZTNA
Zero trust network access (ZTNA) is a security model that assumes that all network traffic is untrusted, regardless of whether it originates from within or outside of the network perimeter. This means that all traffic is subject to the same level of scrutiny and verification, regardless of its origin.
One of the main principles of ZTNA is the idea of “never trust, always verify.” This means that user access to resources is granted only after the user has been authenticated and authorized, and their device has been determined to be compliant with the organization’s security policies.

There are several key components to a zero-trust network access system:
Identity and access management: This involves verifying the identity of users and devices, and granting or denying access to resources based on the user’s role and privileges.
Device compliance: This involves verifying that devices meet the organization’s security standards, such as having up-to-date software, firewalls, and antivirus protection.
Network segmentation: This involves dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments, so that if one segment is compromised, the rest of the network is protected.
Multifactor authentication: This involves requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a security token, in order to access resources.
Continuous monitoring: This involves monitoring network traffic and user activity in real-time, so that any unusual activity can be detected and dealt with promptly.
By implementing a zero trust network access system, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of cyber attacks and data breaches. It is an effective way to protect against both external threats and insider threats, and can help organizations meet compliance requirements and safeguard sensitive data.
We hope you found article interesting. For more exclusive content follow us on Facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn