New BGP Flaws Found in Common Internet Routing Software
A software implementation of the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) has flaws that might be exploited to force vulnerable BGP peers to experience a denial-of-service (DoS) scenario. This information was discovered by cybersecurity researchers.
Version 8.4 of FR Routing, a well-liked open source internet routing protocol suite for Linux and Unix platforms, contains the three vulnerabilities. There are dangers to the supply chain because it is now used by numerous vendors, including NVIDIA Cumulus, DENT, and Sonic.
The discovery is the outcome of Vedere Labs’ examination of seven different BGP implementations: FR Routing, BIRD, Open BGPD, Mikrotik Router OS, Juniper Junos, Cisco IOS, and Arista EOS.
A gateway protocol called BGP is used to communicate reachability and routing information between autonomous systems. It is used to determine the best delivery routes.
The following is a list of the three flaws:
Out-of-bounds read when processing a corrupted BGP OPEN message with an Extended Optional Parameters Length option. CVE-2022-40302 (CVSS score: 6.5).
CVE-2022-40318 (6.5 out of 10) – Out-of-bounds read when a BGP OPEN message with an Extended Optional Parameters Length option is processed incorrectly.
CVE-2022-43681 (6.5 out of 10) – An abruptly ending option length octet in a BGP OPEN message that is faulty causes an out-of-bounds read.
The company stated that the issues could be exploited to achieve a DoS condition on vulnerable BGP peers, allowing a drop across all BGP sessions and routing tables and leaving the peer unresponsive.
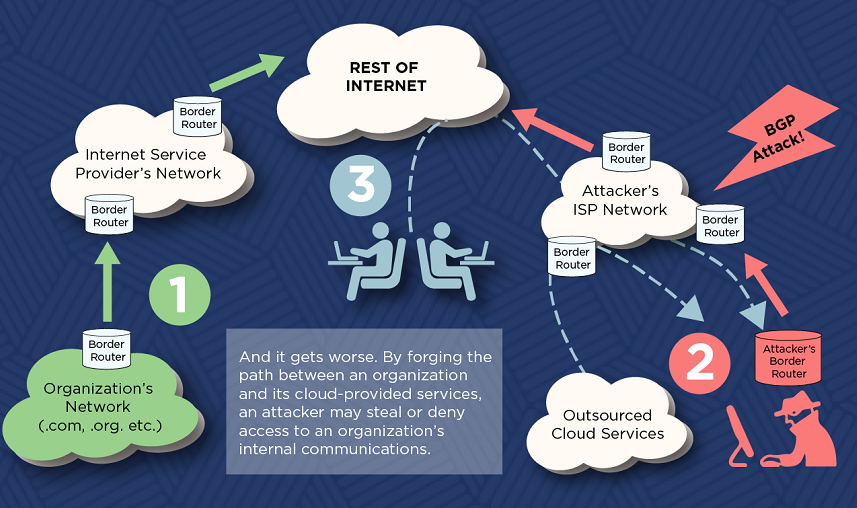
“By delivering faulty packets continually, the DoS condition may last forever. The susceptible code pattern that has been duplicated into numerous functions involved in various stages of parsing OPEN messages is the primary cause.
A threat actor might trick a trustworthy BGP peer’s IP address, compromise a reliable peer using other vulnerabilities and configuration errors, and then send a specially constructed unsolicited BGP OPEN message.
This can be achieved by making use of the fact that “FRRouting begins to process OPEN messages even before getting a chance to verify the BGP Identifier and ASN fields of the originating router.”
Additionally, Forescout has made an open source tool called bgp_boofuzzer available that enables businesses to test the security of the BGP suites they use internally and discover brand-new vulnerabilities in BGP implementations.
The discoveries follow ESET’s discovery a few weeks prior that used routers from business networking settings were hiding important information, including login credentials, VPN information, cryptographic keys, and other crucial client data.
See more: Apple Rolls Out Software patches for iOS iPadOS and macOS
See more: Anonymous Sudan group launched fresh cyber-attack on Israel
We hope you found article interesting. For more exclusive content follow us on Facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn