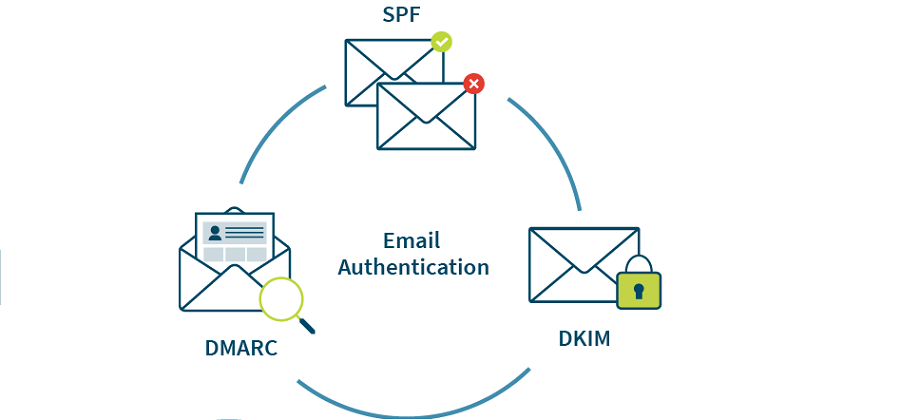
What is email authentication – SPF, DMARC and DKIM
Email authentication is the process of verifying the identity of the sender of an Email and ensuring that the email was not modified during transit. It’s an important security measure that helps prevent email fraud and phishing attacks.
See more: Basics of Email – Email server and its components
There are several email authentication systems in use today, including:
Sender Policy Framework (SPF):
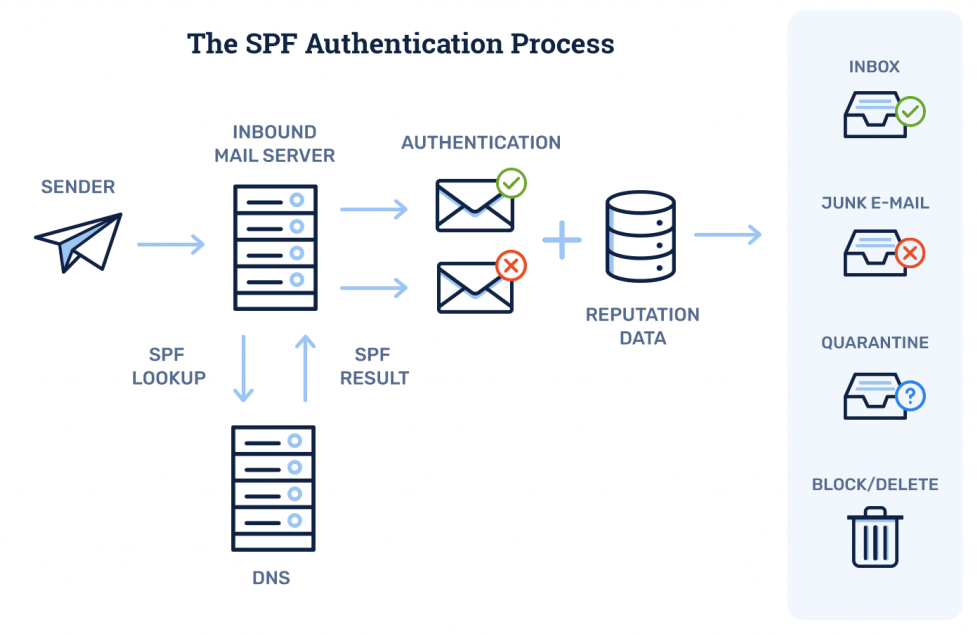
SPF is an email authentication method that allows a receiving mail server to check that incoming mail from a domain is being sent from a valid mail server. The SPF record is stored in the domain’s DNS (Domain Name System) and lists the authorized mail servers for that domain. If an incoming email is not from an authorized mail server, it will be marked as spam or rejected.
Below image explains the SPF authentication process.
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM):
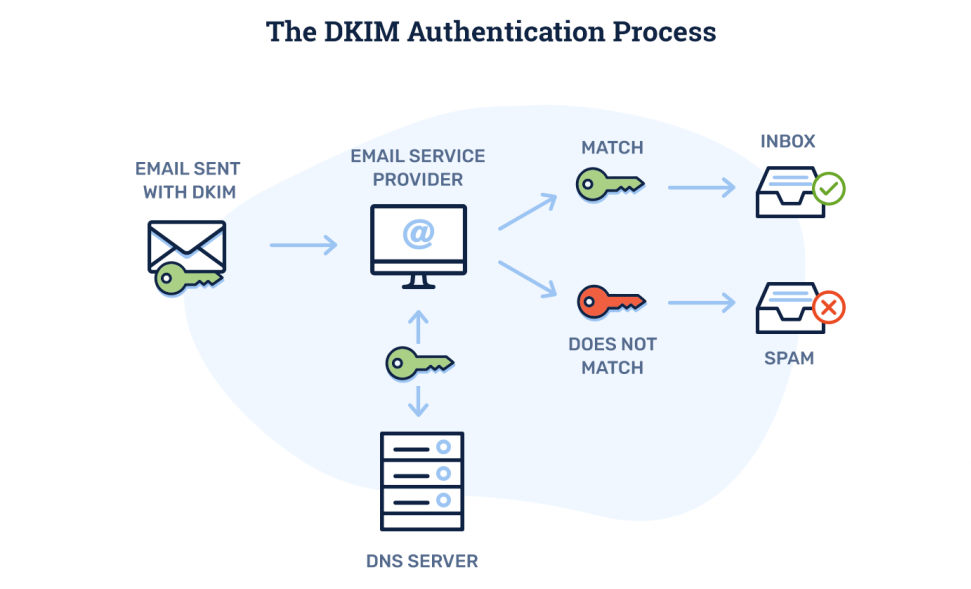
DKIM is an email authentication method that uses digital signatures to verify that an email was not modified in transit. The sender signs the email using a private key, and the recipient verifies the signature using the sender’s public key, which is stored in the domain’s DNS.
Below image explains the DKIM authentication process.
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance (DMARC):
DMARC is an email authentication method that provides a way for senders and receivers to determine the authenticity of emails. DMARC allows a sender to publish a policy in their domain’s DNS that specifies which authentication methods (SPF and/or DKIM) are used to protect their domain and what the recipient should do if the authentication fails (e.g., mark the email as spam or reject it).
Below image explains how DMARC works.

TLS (Transport Layer Security):
TLS is an encryption protocol that provides secure communication over the internet. When used with email, it encrypts the email as it is being transmitted from the sender’s mail server to the recipient’s mail server, ensuring that the email is protected from eavesdropping and tampering.
See more: Top 7 Attacks on Active Directory: What You Need to Know
Using these authentication systems, organizations and individuals can better protect themselves and their customers from email fraud and phishing attacks. By verifying the identity of the sender and ensuring the integrity of the email, email authentication systems help to ensure that emails are delivered securely and can be trusted.
In conclusion, email authentication systems play a critical role in securing email communications. By implementing these systems, organizations and individuals can protect their reputation, confidential information, and customers from email fraud and phishing attacks.
We hope you found article interesting. For more exclusive content follow us on Facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn