Ransomware – its type and countermeasures against ransomware
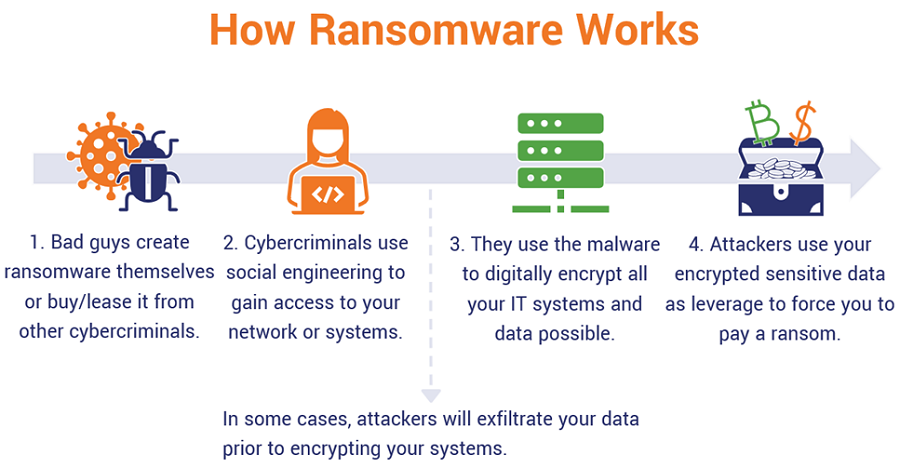
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts the victim’s files and demands payment, typically in cryptocurrency, in exchange for the decryption key. It can be extremely damaging to individuals and organizations, as it can cause significant data loss and potentially even put the victim out of business.
There are several types of ransomwares, including:
WannaCry: WannaCry is a ransomware worm that spreads through a vulnerability in Windows systems. It affected over 200,000 computers in 150 countries in 2017.
Petya: Petya is a ransomware that encrypts the hard drive’s master boot record, making the entire system unusable. It caused significant damage to companies such as Maersk and FedEx in 2017.
Locky: Locky is a ransomware that spreads through email attachments and has been known to use social engineering tactics to trick victims into downloading and executing the malware.
See more: Scammers dupe millions from companies through the “boss scam”
Detecting Ransomware
There are several ways to detect ransomware, including:
Antivirus Software: Antivirus software can detect and block many types of ransomware before they have a chance to encrypt files.
Behavioral Analysis: Behavioral analysis tools can monitor system activity and detect anomalies or suspicious behavior that may indicate the presence of ransomware.
User Education: Educating users on safe browsing habits, such as avoiding suspicious websites and not clicking on suspicious links or email attachments, can help prevent ransomware infections.
Defending Against Ransomware
There are several control measures that can be taken to prevent or mitigate the impact of ransomware, including:
Regular backups: Regular backups of important data can help mitigate the impact of a ransomware infection, allowing data to be restored from a previous, uninfected state.
Network Segmentation: Segregating a network into separate zones with different security requirements can limit the spread of ransomware if an infection occurs.
Patch Management: Keeping software and operating systems up-to-date can help prevent vulnerabilities that can be exploited by ransomware.
User Education: Educating users on safe browsing habits, such as avoiding suspicious websites and not clicking on suspicious links or email attachments, can help prevent ransomware infections.
Incident Response Plan: Having an incident response plan in place can help organizations respond quickly and effectively to a ransomware attack, minimizing the impact and reducing the risk of paying the ransom.
In conclusion, ransomware is a serious threat to individuals and organizations, and can cause significant damage and financial loss. To protect against ransomware, it’s important to use a combination of detection and prevention measures, such as antivirus software, regular backups, network segmentation, patch management, user education, and having an incident response plan in place. By following these best practices, organizations can help reduce the risk of ransomware infections and protect their sensitive data.
See more: What is VPN – Difference between SSL VPN and IPSec VPN
We hope you found article interesting. For more exclusive content follow us on Facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn






